Introduction
In the United States, insurance penetration serves as a critical indicator of the extent to which individuals and businesses are covered by insurance relative to the size of the economy. This relationship between insurance penetration, economic growth, and financial stability is of paramount importance to policymakers, as it influences the overall resilience and sustainability of the nation’s economy.

Insurance and Economic Growth
Role of Insurance in Economic Growth
Insurance plays a pivotal role in promoting economic growth by providing a safety net against risks, thereby fostering investment, entrepreneurship, and productivity. When individuals and businesses are protected against potential losses through insurance coverage, they are more inclined to engage in various economic activities with confidence. For example, entrepreneurs are more likely to start businesses, knowing they have insurance to safeguard their investments against unforeseen events.
Impact on Key Sectors
The impact of insurance on key sectors of the U.S. economy cannot be overstated. In manufacturing, insurance coverage protects businesses from disruptions caused by accidents or natural disasters, ensuring uninterrupted production and supply chains. Similarly, in agriculture, farmers rely on insurance to mitigate risks associated with adverse weather conditions, pests, and crop failures, thereby ensuring food security and stability in agricultural production. Moreover, insurance supports infrastructure development by providing risk transfer mechanisms for construction projects, enabling investments in critical infrastructure such as transportation networks, utilities, and public facilities.
Insurance and Financial Stability
Contribution to Financial Stability
Insurance contributes significantly to financial stability by spreading risks across a broad pool of policyholders and reducing the likelihood of catastrophic losses that could destabilize financial markets. By transferring risks from individuals and businesses to insurance companies, insurance promotes resilience and stability within the financial system. Insurance companies also play a crucial role in maintaining liquidity and solvency, as they hold reserves to meet policyholder obligations in the event of claims.
Regulatory Oversight
Regulatory oversight is essential to ensure the stability and soundness of the insurance sector. In the United States, regulatory agencies such as the National Association of Insurance Commissioners (NAIC) oversee insurance companies’ financial health, compliance with solvency requirements, and consumer protection measures. These regulatory efforts aim to safeguard policyholders’ interests and maintain the stability of the insurance industry.
Barriers to Insurance Penetration
Despite the benefits of insurance, several barriers hinder insurance penetration in the United States, including:
Affordability Constraints
Many individuals and businesses face affordability constraints when purchasing insurance coverage, particularly in areas such as health insurance and property insurance. Rising premiums and out-of-pocket costs can deter people from obtaining adequate coverage, leading to gaps in insurance protection.
Lack of Awareness
A lack of awareness about insurance products and their benefits among certain segments of the population contributes to low insurance penetration rates. Many individuals may underestimate the importance of insurance or have misconceptions about its value, leading to underinsurance or non-insurance.
Regulatory Barriers
Regulatory barriers, such as complex licensing requirements and restrictive underwriting practices, can impede the accessibility of insurance products, particularly for underserved communities and small businesses. Streamlining regulations and promoting market competition can help address these barriers and expand access to insurance coverage.
Cultural Attitudes
Cultural attitudes towards risk and insurance may also influence insurance penetration levels. Some individuals may be averse to purchasing insurance due to cultural beliefs or preferences, leading to low uptake rates. Efforts to promote financial literacy and educate consumers about the benefits of insurance can help overcome cultural barriers to insurance penetration.
Global Perspective on Insurance Penetration
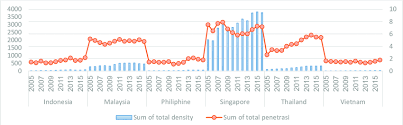
Comparison Across Countries
When comparing insurance penetration levels across countries, the United States typically ranks among the top nations in terms of insurance density and penetration. However, there are significant variations in insurance uptake and economic development across different regions and income levels.
Factors Influencing Insurance Penetration
Variations in economic structures, regulatory environments, and socio-economic factors contribute to differences in insurance penetration levels. Countries with robust regulatory frameworks, high levels of financial literacy, and strong insurance cultures tend to have higher insurance penetration rates.
Future Outlook and Policy Implications
Technological Advancements
Technological advancements, such as artificial intelligence, big data analytics, and digital distribution channels, are transforming the insurance industry by enhancing risk assessment, improving customer engagement, and reducing operational costs. Insurers are increasingly leveraging technology to develop innovative products, streamline processes, and enhance the overall customer experience.
Demographic Shifts
Demographic shifts, including an aging population and changing consumer preferences, are reshaping the insurance landscape. Insurers are adapting their offerings to cater to the needs and preferences of diverse demographic groups, such as millennials, Generation Z, and baby boomers. Moreover, insurers are exploring new distribution channels, such as online platforms and mobile apps, to reach digital-native consumers and enhance accessibility.
Regulatory Developments
Regulatory developments, such as changes in insurance laws and regulations, have significant implications for insurers and policyholders. Insurers must stay abreast of regulatory changes and ensure compliance with evolving requirements to maintain market competitiveness and consumer trust. Moreover, policymakers play a crucial role in shaping the regulatory environment to foster innovation, protect consumers, and promote market stability.
Climate Change and Sustainability
Climate change poses significant risks to the insurance industry and the broader economy, including increased frequency and severity of natural disasters, rising sea levels, and extreme weather events. Insurers are incorporating climate risk into their underwriting and pricing strategies to mitigate potential losses and promote sustainability. Moreover, insurers are exploring opportunities to support climate resilience and adaptation efforts through innovative insurance products, risk management solutions, and investment strategies.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the relationship between insurance penetration, economic growth, and financial stability is complex and multifaceted. By addressing barriers to insurance penetration and promoting policies that support a vibrant and resilient insurance sector, policymakers can contribute to sustainable economic development and financial well-being for individuals and businesses across the United States. Moreover, insurers play a crucial role in promoting resilience, stability, and prosperity by providing risk protection, supporting investments, and facilitating economic growth.

