INTRODUCTION:
In recent years, the advent of food delivery platforms has revolutionized the restaurant industry, offering unparalleled convenience and accessibility to consumers while simultaneously presenting novel challenges and risks for businesses operating within this realm. In the United States, insurance tailored for food delivery platforms plays an indispensable role in mitigating liability and food safety risks, providing comprehensive coverage for a plethora of potential exposures faced by restaurants, delivery drivers, and platform operators.

Liability Coverage
A. Third-Party Liability:
- Bodily Injury: Insurance policies extend coverage for bodily injury claims stemming from accidents involving delivery drivers, customers, or other third parties. This encompasses incidents such as slip-and-fall accidents, collisions, or other mishaps occurring during the delivery process.
- Property Damage: Coverage encompasses property damage claims arising from accidents, such as collisions involving delivery vehicles or damage to customer property during the delivery process. This could include incidents where a delivery driver accidentally damages a customer’s property while making a delivery.
B. Product Liability:
- Food Contamination: Insurance policies may encompass product liability claims associated with foodborne illnesses or contamination. This includes coverage for claims related to medical expenses, lost wages, and pain and suffering resulting from foodborne illness caused by contaminated food delivered via the platform.
- Allergen Risks: Coverage extends to claims arising from allergic reactions or adverse food reactions caused by mislabeling or cross-contamination of food products. This includes incidents where a customer suffers an allergic reaction due to undeclared allergens in the food delivered.
C. Cyber Liability:
- Data Breaches: Policies may include coverage for data breaches or cybersecurity incidents involving customer information stored on the platform’s servers. This encompasses incidents such as unauthorized access to customer accounts or breaches resulting in the exposure of personal data.
- Privacy Violations: Coverage may extend to claims alleging privacy violations, such as improper use of personal data by the platform operator or unauthorized access to customer information. This includes incidents where customer data is mishandled or improperly accessed by platform employees.
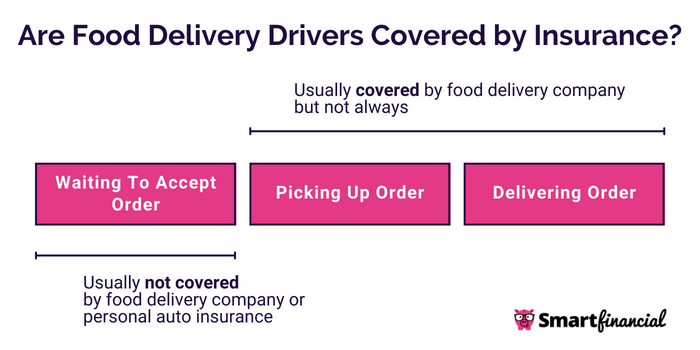
Food Safety Risks
A. Contamination Events:
- Coverage for Food Recalls: Insurance policies may provide coverage for costs associated with food recalls, including product disposal, cleaning, and disinfection of facilities. This includes incidents where contaminated food products necessitate a recall to protect public health.
- Business Interruption: Coverage may extend to business interruption losses resulting from contamination events or regulatory closures. This reimburses the insured for lost revenue and extra expenses incurred to resume operations after a contamination event or closure due to regulatory action.
B. Regulatory Compliance:
- Compliance Costs: Policies may cover expenses related to compliance with food safety regulations, such as training, inspections, and audits conducted by regulatory authorities. This includes costs associated with ensuring that food handling practices comply with regulatory standards.
- Fines and Penalties: Coverage may include reimbursement for fines, penalties, or regulatory sanctions imposed on the insured for violations of food safety laws or regulations. This provides financial protection in the event of regulatory enforcement actions or penalties.

Regulatory Landscape and Compliance
A. Food Safety Regulations:
- Federal Regulations: The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) oversees food safety regulations at the federal level, enforcing standards governing the production, processing, and distribution of food products. This includes regulations aimed at ensuring the safety and integrity of food delivered via platforms.
- State Regulations: State health departments are responsible for enforcing food safety regulations at the state level, including licensing, inspection, and enforcement of food safety laws for restaurants and food service establishments. This includes compliance with state-specific regulations governing food delivery operations.
B. Insurance Requirements:
- Business Insurance: Restaurants and food delivery platforms are typically required to carry commercial general liability (CGL) insurance, which includes coverage for bodily injury, property damage, and product liability claims. This ensures that businesses have financial protection against liability claims arising from their operations.
- Additional Coverage: Some jurisdictions may mandate specific insurance coverage for businesses, such as liquor liability insurance for establishments serving alcohol or commercial auto insurance for delivery vehicles. This ensures that businesses have adequate insurance coverage to address potential risks associated with their operations.
Best Practices and Risk Management
A. Training and Education:
- Food Handling Training: Restaurants and delivery drivers should undergo training in safe food handling practices to prevent contamination and minimize the risk of foodborne illnesses. This ensures that food delivered via the platform meets safety standards and regulatory requirements.
- Cybersecurity Training: Platform operators should educate employees about cybersecurity risks and best practices for protecting customer data. This includes training on how to identify and respond to potential cybersecurity threats to safeguard customer information.
B. Quality Control Measures:
- Food Safety Protocols: Restaurants should implement rigorous food safety protocols, including regular cleaning and sanitization of equipment, proper storage and handling of food products, and temperature control measures. This ensures that food delivered via the platform is safe for consumption and complies with food safety regulations.
- Quality Assurance: Platform operators should conduct regular quality assurance checks to ensure compliance with food safety standards and regulatory requirements. This includes inspections of partner restaurants and delivery vehicles to verify compliance with food safety protocols.
Conclusion
Insurance for food delivery platforms is essential for mitigating liability and food safety risks associated with operating in this dynamic industry. By understanding coverage options, regulatory requirements, and best practices for risk management, restaurants and platform operators can protect their businesses and ensure the safety and satisfaction of their customers. In an ever-evolving landscape, comprehensive insurance coverage remains a cornerstone for the success and resilience of food delivery platforms in the United States.



