Introduction
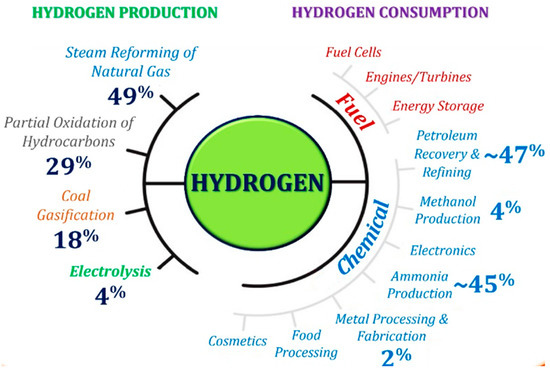
Hydrogen fuel cell technology is a promising clean energy solution that utilizes hydrogen gas to produce electricity through an electrochemical process. It has diverse applications in transportation, such as fuel cell vehicles (FCVs), and energy generation for residential, commercial, and industrial purposes. In the United States, hydrogen fuel cell technology is gaining traction as a key component of efforts to decarbonize transportation and reduce greenhouse gas emissions.

Safety Risk Coverage:
Hydrogen fuel cell technology presents inherent safety risks, primarily related to the storage, transportation, and handling of hydrogen gas. Insurance solutions are essential to mitigate these risks and protect stakeholders, including manufacturers, suppliers, and end-users. Insurers offer specialized coverage for safety risks associated with hydrogen storage facilities, transportation infrastructure, and fueling stations. This coverage encompasses risk assessments, safety protocols, and emergency response measures to prevent accidents and minimize potential losses. Compliance with federal safety regulations, such as those outlined by the Department of Transportation (DOT) and the Occupational Safety and Health Administration (OSHA), is critical to maintaining insurance coverage and ensuring the safe deployment of hydrogen fuel cell technology.
Accident Coverage:
Accidents involving hydrogen fuel cells, such as leaks, fires, or explosions, pose significant financial and legal liabilities for stakeholders. Insurance policies provide coverage for accidents resulting from equipment malfunctions, human error, or external factors, ensuring prompt response and recovery efforts. Coverage may include property damage, bodily injury, environmental remediation, and business interruption losses associated with accidents involving hydrogen fuel cell technology. Insurers work closely with industry participants to assess risk factors, implement preventive measures, and develop contingency plans to mitigate the impact of accidents on both human safety and financial stability.
Regulatory Compliance and Liability:
Compliance with safety regulations and liability coverage are integral aspects of deploying hydrogen fuel cell technology in the United States. Stakeholders must adhere to federal and state regulations governing the production, storage, transportation, and usage of hydrogen gas. This includes compliance with safety standards set forth by regulatory agencies such as the DOT, the National Fire Protection Association (NFPA), and the Environmental Protection Agency (EPA). Liability insurance policies provide coverage for accidents involving hydrogen fuel cell technology, including legal defense costs, settlement payments, and indemnification for third-party claims. Insurers collaborate with industry stakeholders to ensure compliance with regulatory requirements and promote best practices in safety and risk management.
Conclusion:
In conclusion, insurance plays a critical role in facilitating the safe and responsible deployment of hydrogen fuel cell technology in the United States. By offering coverage for safety risks, accidents, and liability exposures, insurers help mitigate financial losses and protect stakeholders across the hydrogen value chain. Under USA policy, insurers work in tandem with industry participants to ensure compliance with safety regulations, promote risk mitigation strategies, and foster the adoption of hydrogen fuel cell technology as a sustainable energy solution for the future.


