Introduction
Life insurance, often seen as a means of ensuring personal financial security, also plays a pivotal role in the expansion and sustainability of businesses, especially in the entrepreneurial landscape of the United States. This essay aims to delve into the multifaceted relationship between life insurance and business expansion, highlighting how life insurance serves as a cornerstone for financial security and growth. By exploring various types of life insurance policies, tax implications, strategies for utilization, and real-world case studies, this essay elucidates the vital role of life insurance in fostering economic prosperity through business expansion.

The Significance of Business Expansion
Business expansion is fundamental to driving economic growth, fostering innovation, and maximizing profitability. In the United States, small businesses are particularly vital, serving as engines of job creation and economic dynamism. Expansion initiatives enable businesses to increase market share, explore new markets, diversify revenue streams, and maintain competitiveness in an ever-evolving business environment. Moreover, business expansion stimulates investment, spurs consumer spending, and contributes significantly to overall economic prosperity.
The Intersection: Life Insurance and Business Expansion
Life insurance intersects with business expansion in various ways, providing critical support for businesses seeking growth and sustainability. Firstly, life insurance offers financial security by safeguarding against unforeseen events such as the loss of key personnel or accumulation of business debt. Additionally, life insurance enhances creditworthiness, facilitates business succession planning, and enables businesses to offer valuable employee benefits. Understanding the intersection between life insurance and business expansion is imperative for entrepreneurs and business owners aiming to leverage life insurance effectively to achieve their growth objectives.
Providing Financial Security
One of the primary roles of life insurance in business expansion is to provide financial security, mitigating risks associated with the loss of key individuals or unforeseen financial liabilities. Key person insurance, for instance, protects businesses against the financial impact of losing key personnel whose expertise or relationships are integral to the company’s success. Similarly, debt protection policies provide a safety net for businesses by ensuring that outstanding debts can be repaid in the event of the death or disability of a key individual.

Enhancing Creditworthiness
Life insurance can also enhance a business’s creditworthiness, enabling access to essential capital for expansion initiatives. Policies with cash value, such as whole life insurance or universal life insurance, can serve as valuable collateral for loans, providing lenders with additional assurance and improving the business’s ability to secure favorable financing terms. By leveraging life insurance as collateral, businesses can access the capital needed to fund expansion projects, invest in growth opportunities, and drive long-term success.
Funding Business Succession
Business succession planning is essential for ensuring continuity and stability in the event of the owner’s death or retirement. Life insurance can play a crucial role in funding buy-sell agreements, providing liquidity to facilitate the smooth transfer of ownership and management responsibilities. In the case of a business owner’s death, life insurance proceeds can be used to buy out the deceased owner’s share of the business, ensuring that the remaining owners retain control and the business can continue operating without disruption.
Types of Life Insurance Policies
- Term Life Insurance:
- Coverage Duration: Term life insurance provides coverage for a specified period, typically ranging from 5 to 30 years.
- Cost-Effectiveness: It offers a cost-effective solution for businesses seeking temporary protection, as premiums are generally lower compared to permanent life insurance policies.
- Renewability: Some term policies may offer the option to renew coverage at the end of the term, although premiums may increase.
- Benefits: If the insured individual passes away during the term, the policy pays out a death benefit to the designated beneficiaries.
- Suitability: Term life insurance is suitable for businesses with short-term financial obligations or those seeking affordable coverage for a specific period, such as to cover a loan or business debt.
- Whole Life Insurance:
- Coverage Duration: Whole life insurance offers permanent coverage for the insured’s entire life, as long as premiums are paid.
- Cash Value Accumulation: It includes a savings component that accumulates cash value over time, offering a guaranteed rate of return.
- Premiums: Premiums remain level throughout the policyholder’s life, providing predictability and stability.
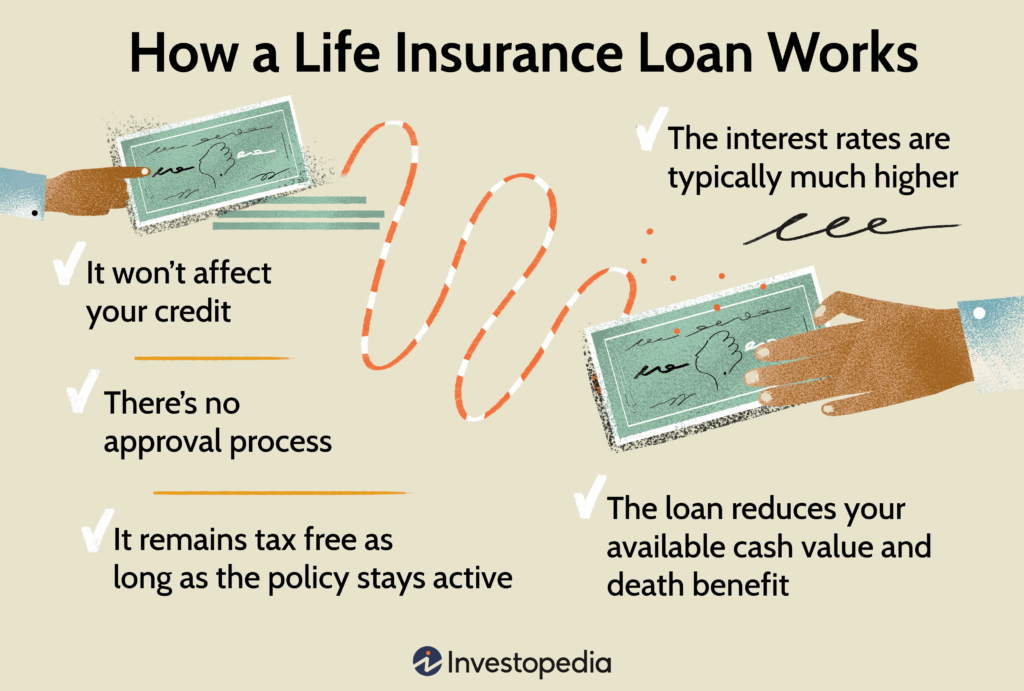
- Benefits: In addition to the death benefit paid out to beneficiaries upon the insured’s death, whole life policies allow policyholders to borrow against the cash value or receive dividends, depending on the policy’s structure.
- Suitability: Whole life insurance is suitable for businesses seeking long-term financial security and asset accumulation, such as funding business succession or providing benefits for key employees.
- Universal Life Insurance:
- Flexibility: Universal life insurance offers flexibility in premium payments and death benefits, allowing policyholders to adjust coverage levels according to changing needs and circumstances.
- Interest Rates: Cash value accumulation is tied to prevailing interest rates, offering the potential for higher returns compared to whole life insurance.
- Premiums: Policyholders have the option to pay premiums in excess of the cost of insurance, which accumulates as cash value and can be used to offset future premiums or fund other financial needs.
- Benefits: Like whole life insurance, universal life policies provide a death benefit to beneficiaries and offer the ability to borrow against the cash value or make withdrawals, subject to certain conditions.
- Suitability: Universal life insurance is suitable for businesses seeking flexibility in premium payments and death benefits, as well as the potential for cash value accumulation and asset diversification.
- Variable Life Insurance:
- Investment Component: Variable life insurance combines life insurance protection with investment opportunities, allowing policyholders to allocate premiums to a variety of investment options such as mutual funds or separate accounts.
- Cash Value: Cash value accumulation is tied to the performance of the underlying investments, offering the potential for higher returns but also greater investment risk compared to other types of life insurance.
- Benefits: Policyholders have the opportunity to grow cash value through market investments and may have access to a wider range of investment options compared to other types of life insurance.
- Suitability: Variable life insurance is suitable for businesses seeking life insurance protection combined with the potential for investment growth, as well as the ability to tailor investment strategies to their specific financial objectives.
Tax Implications of Life Insurance in Business
Understanding the tax implications of life insurance is crucial for businesses seeking to maximize its benefits and minimize tax liabilities. Premium payments for life insurance policies are generally tax-deductible as business expenses, reducing the business’s taxable income and lowering its overall tax burden. Additionally, death benefits paid out to beneficiaries are typically tax-free, providing a source of tax-free liquidity that can be used to fund business succession or repay outstanding debts. However, businesses should be aware of the tax treatment of policy loans and withdrawals, as well as the taxation of cash surrender value upon policy termination. By strategically managing the tax implications of life insurance, businesses can optimize their financial position and leverage life insurance as a valuable tool for business expansion.

Strategies for Leveraging Life Insurance in Business Expansion
Effective utilization of life insurance in business expansion requires strategic planning and implementation. Business continuation planning involves identifying key individuals within the organization and securing adequate life insurance coverage to protect against the financial impact of their loss. Key person coverage strategies aim to mitigate risks associated with the loss of key personnel by providing financial support to the business in the event of their death or disability. Funding buy-sell agreements with life insurance ensures smooth ownership transitions and preserves the business’s continuity in the face of unforeseen events. Deferred compensation planning and executive bonus plans offer additional benefits to key employees, helping businesses attract and retain top talent while fostering a culture of loyalty and commitment.
Case Studies and Examples
Real-world case studies and examples illustrate the practical applications of life insurance in business expansion. For instance, a small manufacturing company may utilize key person insurance to protect against the loss of its chief engineer, whose expertise is critical to the company’s operations. Similarly, a family-owned business may fund a buy-sell agreement with life insurance to ensure a smooth transfer of ownership between generations. These case studies demonstrate how businesses can leverage life insurance to address challenges, seize opportunities, and achieve their growth objectives effectively.
Conclusion
In conclusion, life insurance plays a crucial role in facilitating business expansion by providing financial security, enhancing creditworthiness, funding business succession, and facilitating employee benefits. By understanding the intersection between life insurance and business expansion and implementing effective strategies, businesses can harness the power of life insurance to achieve their growth objectives and ensure long-term success. As businesses continue to navigate the complexities of the modern business landscape, life insurance remains a valuable asset that can drive growth, resilience, and prosperity in the ever-changing business environment.


