Introduction
Estate planning is the process of organizing and managing one’s assets during their lifetime and distributing them after death. It involves various legal and financial strategies to ensure that assets are transferred to intended beneficiaries efficiently and according to the individual’s wishes. Wealth transfer, a key component of estate planning, refers to passing assets to heirs, beneficiaries, or charitable organizations.

Understanding Tax Implications
In the United States, estate taxes and gift taxes are significant considerations in wealth transfer planning:
- Federal Estate Tax: The federal estate tax is a tax on the transfer of property at death. As of 2022, estates valued below $12.06 million for individuals and $24.12 million for married couples are exempt from federal estate tax. Above these thresholds, the tax rate can be as high as 40%. Proper estate planning aims to minimize or eliminate estate tax liability.
- Gift Tax: The gift tax applies to transfers of property during one’s lifetime. Individuals can gift up to a certain amount each year (e.g., $16,000 per recipient in 2022) without incurring gift taxes. Gifts exceeding this annual exclusion may be subject to gift taxes, although a lifetime exemption equivalent to the estate tax exclusion can offset taxable gifts.
Role of Life Insurance in Wealth Transfer
Life insurance can play a crucial role in estate planning and wealth transfer for several reasons:
- Liquidity: Life insurance provides immediate liquidity upon the insured’s death, which can be used to pay estate taxes, debts, funeral expenses, and other obligations without the need to liquidate assets.
- Estate Tax Planning: Life insurance proceeds can be used to cover potential estate tax liabilities, particularly for individuals with larger estates that may exceed the estate tax exemption thresholds.
- Income Replacement: Life insurance can replace lost income for dependents and beneficiaries, ensuring financial stability after the insured’s death.
Types of Life Insurance
Various types of life insurance policies offer different features and benefits suitable for wealth transfer planning:
- Term Life Insurance: Term life insurance provides coverage for a specified period, such as 10, 20, or 30 years. It offers pure death benefit protection without cash value accumulation and is often more affordable for younger individuals.
- Permanent Life Insurance: Permanent life insurance, including whole life, universal life, and variable life, offers coverage for the insured’s entire life, as long as premiums are paid. These policies accumulate cash value over time, providing a tax-deferred savings component in addition to the death benefit.
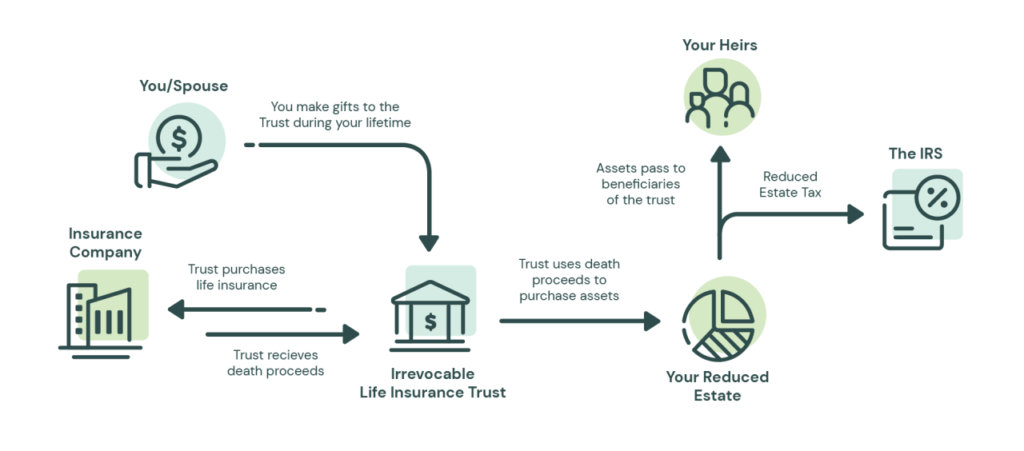
- Irrevocable Life Insurance Trust (ILIT): An ILIT is a trust specifically designed to own life insurance policies on the insured’s life. By transferring ownership of the policy to the trust, the proceeds can be excluded from the insured’s estate, potentially reducing estate taxes.
Estate Planning Strategies Using Life Insurance
Several estate planning strategies leverage life insurance to facilitate tax-efficient wealth transfer:
- Irrevocable Life Insurance Trust (ILIT): Establishing an ILIT can help remove life insurance proceeds from the insured’s estate, thereby minimizing estate tax exposure. The trust owns the policy, and the proceeds are distributed to beneficiaries according to the trust terms.
- Gifts of Premiums: Individuals can gift money to an ILIT to pay life insurance premiums, leveraging annual gift tax exclusions to fund the policy without incurring gift taxes.
- Estate Equalization: Life insurance can be used to equalize inheritances among beneficiaries, particularly when certain assets are difficult to divide or when one beneficiary will inherit a business or real estate property.
- Charitable Giving: Life insurance can facilitate charitable giving by naming a charitable organization as the policy beneficiary. This allows individuals to support charitable causes while potentially receiving estate tax benefits.
Tax Considerations and Optimization Strategies
Maximizing tax efficiency in life insurance-based wealth transfer requires careful planning and consideration of various factors:
- Estate Tax Exemption: Taking full advantage of the federal estate tax exemption can help minimize estate tax liabilities. Proper estate planning may involve strategies to leverage exemptions for both individuals and married couples.
- Gift Tax Strategies: Utilizing annual gift tax exclusions and lifetime gift tax exemptions can reduce the size of the taxable estate and maximize wealth transfer to heirs.
- Income Taxation of Life Insurance: While life insurance proceeds are generally income tax-free to beneficiaries, certain policy withdrawals, loans, or surrenders may trigger taxable events. Understanding the tax implications of life insurance transactions is essential for effective wealth transfer planning.
- State-Specific Considerations: In addition to federal taxes, individuals must consider state estate taxes, inheritance taxes, and other local regulations, as these can vary significantly by state.
Practical Considerations and Implementation
Implementing a tax-efficient wealth transfer strategy using life insurance involves several practical considerations:
- Policy Selection: Choosing the right type and amount of life insurance coverage based on individual needs, financial goals, and estate planning objectives is essential.
- Policy Ownership and Beneficiary Designations: Properly structuring the ownership and beneficiary designations of life insurance policies can help achieve tax efficiency and avoid unintended consequences.
- Regular Review and Updates: Estate planning strategies should be reviewed periodically to ensure they remain aligned with changing financial circumstances, tax laws, and personal objectives.
- Professional Guidance: Working with qualified professionals, such as estate planning attorneys, tax advisors, and insurance specialists, is crucial for developing and implementing an effective wealth transfer plan.
Conclusion
In conclusion, passing assets to heirs tax-efficiently using life insurance requires careful planning, consideration of tax implications, and implementation of appropriate estate planning strategies. By leveraging various types of life insurance policies, establishing trusts, and maximizing available tax exemptions, individuals can transfer wealth to future generations while minimizing estate tax liabilities and ensuring financial security for their loved ones. Professional guidance and regular review of estate plans are essential to navigate the complexities of tax laws and achieve optimal outcomes in wealth transfer planning.



