INTRODUCTION:
Calculating life insurance coverage needs is a critical financial planning task for individuals and families. Life insurance provides financial protection to dependents in the event of the insured’s death, helping to cover various expenses and maintain their standard of living. Determining the appropriate amount of coverage requires careful consideration of several factors, including current financial obligations, future expenses, and long-term goals. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll explore the process of calculating life insurance coverage needs in detail, covering key concepts, methods, and considerations.
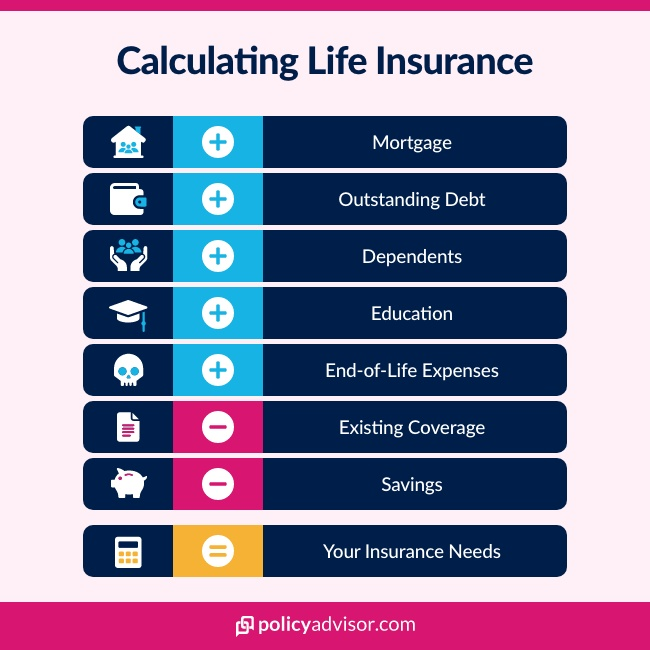
Understanding Life Insurance
Life insurance is a contract between an individual (the insured) and an insurance company, where the insurer agrees to pay a specified amount of money (the death benefit) to designated beneficiaries upon the insured’s death. In exchange, the insured pays regular premiums to the insurer. Life insurance serves multiple purposes, including:
- Income Replacement: Life insurance can replace lost income, ensuring that dependents have financial support after the insured’s death.
- Debt Repayment: It can be used to pay off outstanding debts such as mortgages, loans, or credit card balances.
- Funeral Expenses: Life insurance proceeds can cover funeral and burial expenses, relieving financial strain on surviving family members.
- Education Funding: It can provide funds for children’s education expenses, including tuition fees and other educational costs.
- Estate Planning: Life insurance can facilitate estate planning by providing liquidity to pay estate taxes or equalize inheritances among beneficiaries.
Factors Influencing Coverage Needs
Several factors influence the amount of life insurance coverage an individual or family requires. Understanding these factors is essential for accurate calculation:
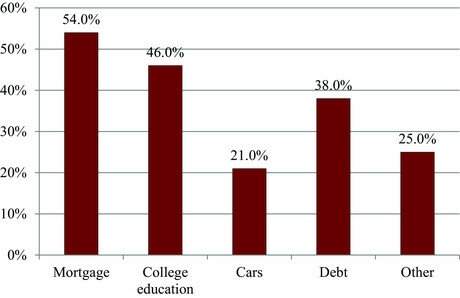
- Income: The insured’s income is a crucial factor in determining coverage needs. Life insurance should ideally replace the insured’s income for a certain period to maintain the family’s standard of living.
- Current Debts: Outstanding debts such as mortgages, loans, and credit card balances should be factored into the coverage amount to ensure they can be paid off in the event of the insured’s death.
- Future Expenses: Anticipated future expenses, including children’s education costs, healthcare expenses, and retirement savings goals, should be considered when calculating coverage needs.
- Existing Assets: Existing savings, investments, and other assets that can be used to support dependents should be taken into account to determine the gap that life insurance needs to fill.
- Inflation: Future inflation rates should be considered to ensure that the coverage amount retains its purchasing power over time.
- Other Sources of Income: Any other sources of income, such as Social Security benefits or survivor benefits, should be factored into the calculation to determine the amount of additional coverage needed.
Methods of Calculating Coverage Needs
Several methods can be used to calculate life insurance coverage needs, each offering different levels of complexity and accuracy. Some common methods include:
- Multiple of Income: This method involves multiplying the insured’s annual income by a certain factor (e.g., 5 to 10 times annual income) to determine the coverage amount. While straightforward, this method may not account for specific financial needs and obligations.
- Human Life Value: The Human Life Value (HLV) method calculates the present value of the insured’s future earnings potential, taking into account factors such as age, occupation, and earning capacity. This method provides a more comprehensive assessment of coverage needs but requires detailed financial analysis.
- Needs Analysis: The Needs Analysis approach involves identifying specific financial needs and obligations (e.g., debt repayment, education funding, funeral expenses) and estimating the amount required to meet each need. The total of these needs represents the required coverage amount.
- Budget-Based Method: This method involves estimating the insured’s ongoing expenses and financial goals and calculating the coverage needed to replace lost income and cover future expenses. It requires a detailed budgeting process but provides a tailored approach to determining coverage needs.
Steps in Calculating Coverage Needs
Regardless of the method used, calculating life insurance coverage needs typically involves the following steps:
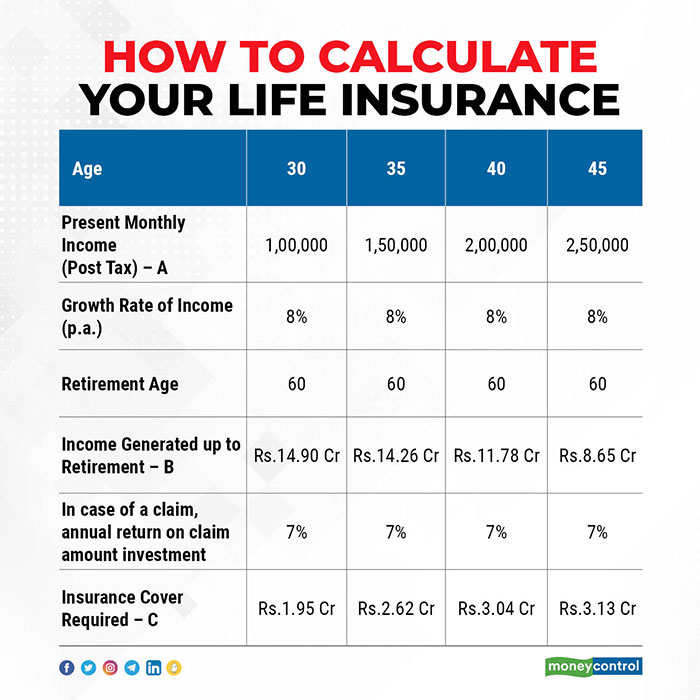
- Assess Financial Situation: Gather information about the insured’s current financial situation, including income, debts, assets, expenses, and financial goals.
- Identify Financial Needs: Identify the insured’s financial needs and obligations, including debt repayment, ongoing expenses, education funding, and other future expenses.
- Estimate Future Expenses: Estimate the amount required to meet future financial obligations, taking into account factors such as inflation and expected changes in expenses over time.
- Calculate Coverage Gap: Determine the difference between the insured’s existing resources (e.g., savings, investments) and the total amount required to meet financial needs. This represents the coverage gap that needs to be filled by life insurance.
- Select Coverage Amount: Based on the calculated coverage gap and the chosen method of calculation, determine the appropriate amount of life insurance coverage needed to adequately protect dependents and achieve financial goals.
- Review and Adjust: Regularly review and adjust the coverage amount as financial circumstances change, such as significant life events (e.g., marriage, birth of children, career changes) or changes in financial goals.
Additional Considerations
When calculating life insurance coverage needs, several additional considerations should be taken into account:
- Health and Lifestyle Factors: The insured’s health, lifestyle habits (e.g., smoking), and medical history can impact both insurability and premium rates. Consideration should be given to these factors when selecting coverage.
- Policy Types and Riders: Understand the different types of life insurance policies (e.g., term life, whole life, universal life) and optional policy riders (e.g., disability income rider, accelerated death benefit rider) that can provide additional benefits and flexibility.
- Tax Implications: Life insurance proceeds are generally received tax-free by beneficiaries. However, certain estate planning considerations and tax implications may apply, particularly for large estates.
- Review Periodically: Life insurance needs can change over time due to factors such as changes in income, expenses, or family circumstances. It’s essential to review coverage periodically and adjust as needed to ensure it remains adequate.
Conclusion
Calculating life insurance coverage needs is a crucial aspect of financial planning, ensuring that dependents are adequately protected in the event of the insured’s death. By considering factors such as income, debts, expenses, and financial goals, individuals can determine the appropriate amount of coverage needed to provide financial security for their loved ones. Whether using simple rules of thumb or more sophisticated financial analysis techniques, the key is to tailor the coverage amount to specific needs and circumstances, reviewing and adjusting regularly as financial circumstances change. With careful planning and consideration, individuals can make informed decisions to protect their families and achieve their long-term financial goals through life insurance.

