Introduction:
In the ever-evolving landscape of healthcare in the United States, few topics have garnered as much attention and concern as the trends in health insurance premiums. Over the past decade, the nation has witnessed significant shifts in the cost of health insurance coverage, impacting individuals, families, employers, and policymakers alike. From fluctuations driven by regulatory changes to the underlying factors influencing premium growth, understanding these trends is crucial for comprehending the broader dynamics of the healthcare system.
This blog aims to provide a comprehensive analysis of the trends in health insurance premiums over the past decade, exploring the factors contributing to their rise, the impact on various stakeholders, and potential strategies for addressing affordability challenges.
The Historical Context:
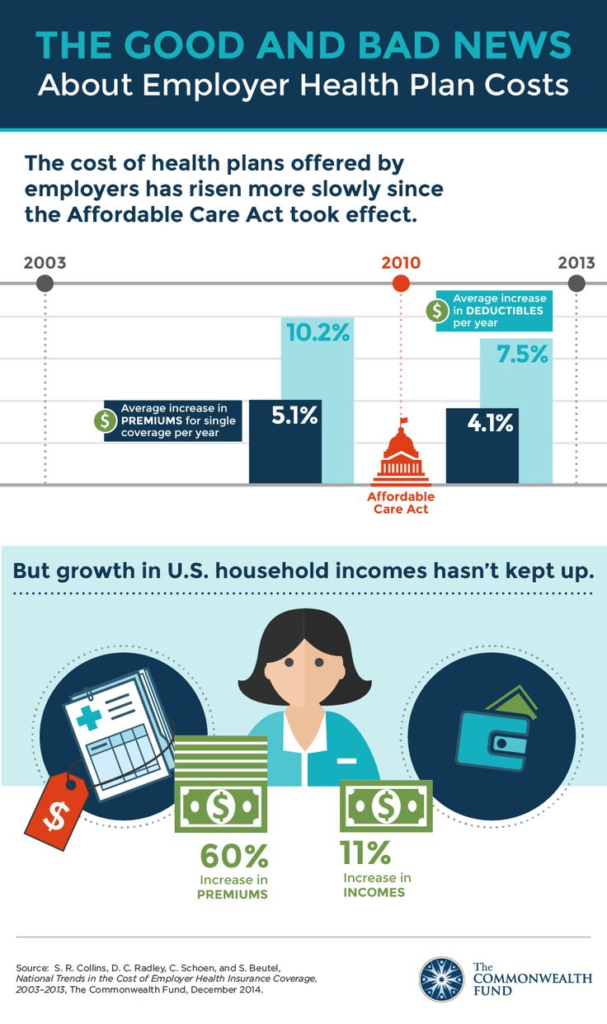
To contextualize the trends in health insurance premiums, it’s essential to examine the historical backdrop against which they have unfolded. Over the past decade, the U.S. healthcare system has experienced significant transformations, including the implementation of the Affordable Care Act (ACA), demographic shifts, technological advancements, and changes in healthcare delivery models.
The ACA, signed into law in 2010, aimed to expand access to health insurance coverage, enhance consumer protections, and control healthcare costs. While the law led to a historic reduction in the uninsured rate, its impact on premiums varied across different segments of the market. Provisions such as guaranteed issue and community rating requirements altered the risk pool composition, influencing premium dynamics for both individual and small group markets.
Additionally, demographic trends, such as an aging population and the rise of chronic conditions, exerted pressure on healthcare utilization and costs. Technological innovations, including the adoption of electronic health records and the proliferation of telemedicine, introduced new opportunities and challenges in healthcare delivery and reimbursement. Furthermore, the shift towards value-based care models incentivized providers to focus on quality and outcomes rather than volume, reshaping reimbursement structures and care delivery approaches.
Factors Driving Premium Growth:
Several factors have contributed to the upward trajectory of health insurance premiums over the past decade, reflecting the complex interplay of market forces, regulatory changes, and underlying cost drivers.
- Medical Inflation: One of the primary drivers of premium growth is medical inflation, which encompasses the rising costs of healthcare services, prescription drugs, and medical technologies. Healthcare spending in the U.S. has consistently outpaced inflation, driven by factors such as advances in medical treatments, increased demand for healthcare services, and administrative overhead.
- Prescription Drug Costs: The escalating prices of prescription drugs have emerged as a significant cost driver in healthcare spending. Pharmaceutical companies often cite research and development costs, regulatory requirements, and the need to recoup investments as reasons for high drug prices. However, concerns about the lack of price transparency, market consolidation, and the role of intermediaries have fueled debates over prescription drug affordability.
- Administrative Overhead: The complexity of the U.S. healthcare system contributes to substantial administrative costs, including billing, coding, and claims processing. Administrative overhead consumes a significant portion of healthcare expenditures, diverting resources away from direct patient care. Streamlining administrative processes and reducing inefficiencies could potentially alleviate some of the cost burdens associated with health insurance premiums.
- Risk Pool Dynamics: The composition of the risk pool plays a crucial role in determining premium rates, particularly in the individual and small group markets. Adverse selection, whereby sicker individuals are more likely to enroll in coverage, can lead to higher premiums as insurers adjust for increased medical costs. Efforts to stabilize risk pools through risk adjustment mechanisms and reinsurance programs aim to mitigate the impact of adverse selection on premiums.
- Regulatory Changes: Policy decisions and regulatory changes at the federal and state levels have influenced premium trends in the health insurance market. Reforms such as the elimination of the individual mandate penalty, expansion of short-term health plans, and changes to essential health benefits requirements have introduced uncertainty and volatility into the market, affecting insurers’ pricing strategies and consumer choices.
- Market Consolidation: The consolidation of healthcare providers and insurers has raised concerns about market competition and its impact on pricing and consumer choice. Mergers and acquisitions among insurers can lead to market concentration, reducing competition and bargaining power for consumers. Similarly, provider consolidation can result in higher prices and decreased negotiating leverage for insurers, ultimately driving up premiums.
Impact on Stakeholders:
The rising cost of health insurance premiums has far-reaching implications for various stakeholders within the healthcare ecosystem, including individuals, families, employers, insurers, and policymakers.
- Individuals and Families: For many individuals and families, the affordability of health insurance premiums is a significant concern when selecting coverage options. Higher premiums may strain household budgets, forcing some individuals to forgo coverage or opt for plans with limited benefits and higher cost-sharing requirements. The trade-off between premiums and out-of-pocket costs can influence healthcare utilization patterns and access to care, particularly for low- and middle-income households.
- Employers: Employer-sponsored health insurance remains a cornerstone of the U.S. healthcare system, covering a significant portion of the population. However, the rising cost of health insurance premiums poses challenges for employers, particularly small businesses, which may struggle to absorb increases in premium costs. Rising healthcare expenses can impact business profitability, hiring decisions, and overall economic competitiveness, prompting employers to explore cost-sharing arrangements, alternative coverage models, and wellness initiatives.
- Insurers: Health insurance companies navigate a complex landscape of regulatory requirements, market dynamics, and consumer expectations when setting premium rates. Rising healthcare costs, coupled with regulatory uncertainty and market volatility, pose challenges for insurers in balancing affordability with profitability. Insurers may respond to premium growth by adjusting benefit designs, expanding provider networks, or implementing cost-containment measures such as utilization management and care coordination programs.
- Policymakers: Policymakers at the federal and state levels play a central role in shaping the regulatory framework governing health insurance premiums. Efforts to address affordability concerns may involve policy interventions such as subsidy programs, reinsurance mechanisms, and price regulation. Additionally, initiatives to promote transparency, competition, and value-based care models aim to align incentives and drive down healthcare costs. However, achieving consensus on comprehensive healthcare reform remains a formidable challenge, given the diverse interests and stakeholders involved.
Strategies for Addressing Affordability Challenges:
Addressing the affordability of health insurance premiums requires a multifaceted approach that addresses underlying cost drivers, promotes competition, and enhances consumer choice and transparency. Several strategies hold promise for mitigating premium growth and improving access to affordable coverage:

- Cost Containment Measures: Implementing cost-containment measures such as value-based care models, care coordination programs, and payment reforms can incentivize providers to deliver high-quality, cost-effective care. By aligning financial incentives with positive health outcomes, these initiatives aim to bend the cost curve and reduce unnecessary healthcare spending.
- Price Transparency: Enhancing price transparency in healthcare can empower consumers to make informed decisions about their healthcare choices, including provider selection, treatment options, and prescription drug purchases. Price transparency tools, such as cost estimator tools and price comparison websites, enable consumers to compare prices and quality metrics across different providers and facilities, fostering competition and driving down costs.
- Competition and Market Innovation: Promoting competition and market innovation in the health insurance industry can stimulate product differentiation, improve customer service, and lower premiums through increased efficiency and productivity. Initiatives such as state-based health insurance exchanges, regulatory reforms, and antitrust enforcement measures aim to create a level playing field for insurers and foster innovation in benefit design and delivery models.
- Consumer Empowerment: Empowering consumers with information, resources, and support can enable them to navigate the complexities of the healthcare system and make choices that align with their healthcare needs and preferences. Education initiatives, enrollment assistance programs, and decision support tools help individuals and families understand their coverage options, rights, and responsibilities, fostering a more active and engaged healthcare consumer base.
- Targeted Subsidies and Assistance: Providing targeted subsidies and financial assistance to low- and middle-income individuals can help make health insurance coverage more affordable and accessible. Subsidy programs such as premium tax credits, cost-sharing reductions, and Medicaid expansion provide financial support to eligible individuals and families, reducing their out-of-pocket expenses and facilitating enrollment in comprehensive coverage options.
Conclusion:
The trends in health insurance premiums over the past decade reflect the dynamic and multifaceted nature of the U.S. healthcare system, shaped by a complex interplay of economic, regulatory, and demographic factors. While premium growth has moderated in recent years, affordability remains a persistent challenge for many individuals, families, and employers.
Addressing the root causes of premium growth requires a coordinated and holistic approach that encompasses cost containment, transparency, competition, and consumer empowerment. By aligning incentives, promoting innovation, and fostering collaboration among stakeholders, policymakers and industry leaders can work towards a more sustainable and equitable healthcare system that delivers high-quality, affordable coverage for all Americans.