Introduction:
Insurance fraud is a pervasive and costly crime that impacts individuals, businesses, and the economy on a global scale. While often overlooked in discussions of crime, its ramifications are significant, leading to increased premiums, financial losses, and strains on the insurance industry. In this blog post, we will delve into the world of insurance fraud, examining its various forms, the methods used by fraudsters, and the efforts underway to combat this insidious problem.
Insurance fraud is not a victimless crime; it affects everyone involved in the insurance process. Policyholders pay higher premiums to offset the losses incurred by fraudulent claims, while insurers face mounting financial burdens and challenges in detecting and preventing fraud. Additionally, the broader economy suffers as resources are diverted towards investigating and prosecuting fraudulent activities, rather than being allocated to productive endeavors.

Despite the widespread impact of insurance fraud, it often flies under the radar, overshadowed by more sensationalized crimes. However, the scale and complexity of insurance fraud demand attention and action. By shining a spotlight on this issue and raising awareness about its consequences, we can empower individuals, businesses, and policymakers to take proactive measures to combat fraud and safeguard the integrity of the insurance system.
Throughout this blog post, we will explore the various forms of insurance fraud, from falsifying claims to staging accidents and inflating damages. We will delve into the motivations behind insurance fraud and the tactics used by fraudsters to exploit vulnerabilities in the system. Additionally, we will examine the innovative strategies and technologies being deployed to detect and prevent fraud, as well as the collaborative efforts underway to address this ongoing challenge.
By gaining a deeper understanding of insurance fraud and its implications, we can work together to disrupt fraudulent activities, protect honest policyholders, and preserve the trust and stability of the insurance industry. Join us on this journey as we uncover the complexities of insurance fraud and explore the ways in which we can combat this pervasive problem. Together, we can build a more resilient and equitable insurance system for all.
Chapter 1:Understanding Insurance Fraud
Understanding Insurance Fraud Insurance fraud occurs when individuals or groups intentionally deceive insurers to obtain financial benefits to which they are not entitled. This deception can take many forms, including falsifying claims, staging accidents, or inflating damages. Healthcare, auto, property, and life insurance are all susceptible to fraud. By understanding the motivations behind insurance fraud and the tactics used by fraudsters, we can better combat this crime.
Insurance fraud is a pervasive and costly crime that occurs when individuals or groups intentionally deceive insurers to obtain financial benefits to which they are not entitled. This deception can manifest in various forms, including falsifying claims, staging accidents, or inflating damages. Insurance fraud spans across different types of insurance, including healthcare, auto, property, and life insurance. By understanding the motivations behind insurance fraud and the tactics used by fraudsters, we can better combat this crime and protect the integrity of the insurance system.
- Definition of Insurance Fraud:
- Insurance fraud involves any deliberate act committed with the intent to deceive an insurer for financial gain. This can include submitting false or exaggerated claims, staging accidents, or providing misleading information to obtain insurance coverage.
- Fraudulent activities can occur at any stage of the insurance process, from the initial application and underwriting process to the filing of claims and subsequent investigations.
- Forms of Insurance Fraud:
- Falsifying claims: Fraudsters may fabricate or exaggerate claims to receive compensation for losses that did not occur or were not as severe as reported.
- Staging accidents: Individuals may orchestrate accidents or collisions to create opportunities for fraudulent claims, such as faking injuries or property damage.
- Inflating damages: Fraudsters may inflate the cost of repairs or medical treatments to receive higher payouts from insurers.
- Premium fraud: Policyholders may provide false information or manipulate their coverage to obtain lower premiums, resulting in financial losses for insurers.
- Susceptible Insurance Types:

- Healthcare insurance: Fraudulent activities in healthcare insurance can include billing for services not rendered, upcoding medical procedures, or prescribing unnecessary treatments.
- Auto insurance: Common auto insurance fraud schemes include staged accidents, vehicle theft, and exaggerated injury claims.
- Property insurance: Fraudulent property insurance claims may involve arson, vandalism, or deliberate damage to property to collect insurance proceeds.
- Life insurance: Fraudulent life insurance claims may involve faking death or providing false information about medical history or beneficiaries.
- Motivations Behind Insurance Fraud:
- Financial gain: The primary motivation for insurance fraud is often financial, with individuals seeking to obtain compensation or benefits to which they are not entitled.
- Financial desperation: Some individuals may turn to insurance fraud out of desperation due to financial difficulties or mounting debts.
- Greed: Others may engage in fraud out of greed, exploiting insurance policies for personal gain without regard for the consequences.
- Perceived injustices: In some cases, individuals may justify fraudulent behavior as a form of retaliation against insurers or perceived adversaries.
In summary, insurance fraud is a deliberate act of deception aimed at obtaining financial benefits through fraudulent means. It encompasses various forms and can affect different types of insurance. Understanding the motivations behind insurance fraud and the tactics used by fraudsters is essential for developing effective prevention and detection strategies. By combating insurance fraud, we can protect the integrity of the insurance system and ensure fair and equitable treatment for all policyholders.
Chapter 2: The Cost of Insurance Fraud
The Cost of Insurance Fraud The financial impact of insurance fraud is staggering, with estimates suggesting it costs billions of dollars annually. These costs are passed on to consumers in the form of higher premiums, making insurance less accessible and affordable for everyone. By examining the economic consequences of insurance fraud, we can grasp the extent of its impact on insurers, policyholders, and the economy at large.
Insurance fraud exacts a heavy toll on both insurers and policyholders, with its financial impact reverberating throughout the economy. The staggering costs associated with insurance fraud, estimated to be in the billions of dollars annually, paint a stark picture of its pervasive influence.
These costs are not borne solely by insurance companies; they are ultimately passed on to consumers in the form of higher premiums. As fraudulent claims drive up the expenses incurred by insurers, they are compelled to adjust their pricing structures to mitigate these losses. Consequently, honest policyholders find themselves shouldering the burden of increased premiums, making insurance less accessible and affordable for everyone.
The economic consequences of insurance fraud extend beyond the immediate financial losses incurred by insurers and policyholders. They ripple throughout the economy, affecting businesses, governments, and society at large. As insurance premiums rise, businesses face higher operating costs, reducing their competitiveness and potentially leading to job losses. Governments are also impacted, as they allocate resources to combat insurance fraud and address its broader societal implications.
Moreover, the corrosive effects of insurance fraud undermine the integrity of the insurance industry, eroding trust and confidence among consumers. When fraudulent claims go undetected or unpunished, it undermines the credibility of insurers and undermines the effectiveness of insurance as a risk management tool.
By examining the economic consequences of insurance fraud, we gain a clearer understanding of its profound impact on insurers, policyholders, and the economy at large. Addressing this issue requires concerted efforts from all stakeholders, including insurers, regulators, law enforcement agencies, and consumers. By implementing robust fraud detection and prevention measures, enhancing regulatory oversight, and promoting public awareness, we can mitigate the financial losses associated with insurance fraud and safeguard the affordability and accessibility of insurance for all.
Chapter 3:Who Commits Insurance Fraud?
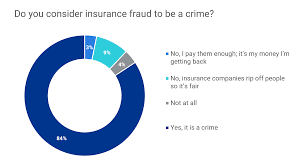
Who Commits Insurance Fraud? Contrary to popular belief, insurance fraud is not limited to stereotypical criminals. Perpetrators come from all walks of life, including professionals like doctors, lawyers, and insurance agents. Motivations for committing insurance fraud vary, from financial desperation to greed and a sense of entitlement. Understanding the diverse profiles of fraudsters is crucial for developing effective prevention and detection strategies.
Contrary to popular belief, insurance fraud is not limited to stereotypical criminals. While there may be individuals who fit the traditional image of fraudsters, the reality is that perpetrators come from all walks of life, including professionals like doctors, lawyers, and insurance agents. The motivations for committing insurance fraud are as diverse as the perpetrators themselves, ranging from financial desperation to greed and a sense of entitlement.
One of the most significant misconceptions about insurance fraud is that it is primarily perpetrated by career criminals or individuals facing dire financial circumstances. While these scenarios certainly occur, they represent only a fraction of the overall picture. In reality, insurance fraud can be committed by individuals from all socioeconomic backgrounds and professions.
Professionals such as doctors, lawyers, and insurance agents may be particularly susceptible to engaging in fraudulent activities due to their intimate knowledge of the insurance system and the potential financial incentives involved. For example, doctors may overbill for medical services, lawyers may stage accidents or inflate damages in personal injury cases, and insurance agents may falsify policy information or submit bogus claims on behalf of clients.
Motivations for committing insurance fraud can vary widely. Some individuals may be driven by financial desperation, resorting to fraudulent schemes as a means of overcoming financial difficulties or maintaining a certain standard of living. Others may be motivated by greed, seeking to exploit insurance policies for personal gain without regard for the consequences. Additionally, a sense of entitlement or perceived injustice may lead some individuals to justify fraudulent behavior as a means of “getting back” at insurance companies or perceived adversaries.
Understanding the diverse profiles of insurance fraudsters is crucial for developing effective prevention and detection strategies. By recognizing that perpetrators can come from any background and may have various motivations, insurers, law enforcement agencies, and regulatory bodies can implement targeted measures to identify and deter fraudulent activity.
Effective prevention and detection strategies may include enhanced data analytics and predictive modeling to identify suspicious patterns, increased oversight and auditing of high-risk professions, and public awareness campaigns to educate consumers about the consequences of insurance fraud. Additionally, collaboration between insurers, law enforcement agencies, and industry associations can help facilitate information sharing and coordination in combating fraud.
Chapter 4:Detecting and Preventing Insurance Fraud:
Detecting and Preventing Insurance Fraud Detecting and preventing insurance fraud requires a multi-pronged approach involving collaboration between insurers, law enforcement agencies, and regulatory bodies. Utilizing data analytics, predictive modeling, anti-fraud software, and investigative techniques can help identify fraudulent activity. Additionally, public awareness campaigns and education efforts empower consumers to recognize and report suspicious behavior.
Detecting and preventing insurance fraud requires a multi-pronged approach involving collaboration between insurers, law enforcement agencies, and regulatory bodies. By leveraging a combination of advanced technology, investigative techniques, and public awareness campaigns, stakeholders can effectively combat fraudulent activity and protect the integrity of the insurance system.

- Utilizing Data Analytics and Predictive Modeling:
- Insurers can harness the power of data analytics and predictive modeling to identify patterns and anomalies indicative of potential fraud. By analyzing vast amounts of data, including claims histories, medical records, and financial transactions, insurers can detect suspicious behavior and flag high-risk cases for further investigation.
- Predictive modeling techniques, such as machine learning algorithms, can help predict the likelihood of fraud based on historical data and patterns. By identifying red flags early on, insurers can take proactive measures to prevent fraudulent claims from being processed.
- Anti-Fraud Software and Investigative Techniques:
- Anti-fraud software solutions provide insurers with tools and resources to streamline fraud detection and investigation processes. These platforms often include features such as case management, data integration, and fraud scoring algorithms to prioritize and manage suspicious claims effectively.
- Investigative techniques, such as surveillance, background checks, and forensic analysis, play a crucial role in uncovering fraudulent activity. Trained investigators work diligently to gather evidence, interview witnesses, and build cases against perpetrators, ultimately leading to prosecution and restitution.
- Collaboration and Information Sharing:
- Collaboration between insurers, law enforcement agencies, and regulatory bodies is essential for effectively combating insurance fraud. By sharing information, resources, and best practices, stakeholders can coordinate efforts to identify and prosecute fraudsters across jurisdictions.
- Industry associations and task forces dedicated to combating insurance fraud facilitate collaboration and information sharing among stakeholders. These collaborative efforts strengthen the collective response to fraud and enhance the overall effectiveness of anti-fraud initiatives.
- Public Awareness Campaigns and Education Efforts:
- Public awareness campaigns and education efforts play a crucial role in empowering consumers to recognize and report suspicious behavior. By educating policyholders about the consequences of insurance fraud and the importance of integrity in the insurance system, stakeholders can foster a culture of honesty and accountability.
- Educational initiatives may include workshops, seminars, and online resources designed to inform consumers about common types of fraud, warning signs to watch for, and steps to take if they suspect fraudulent activity. By empowering consumers to take an active role in combating fraud, stakeholders can create a united front against fraudulent behavior.
Chapter 5: Legal and Ethical Implications

Legal and Ethical Implications Insurance fraud carries significant legal and ethical ramifications. Convicted individuals may face criminal charges, civil penalties, and reputational damage. Legal frameworks at the state and federal levels, along with industry regulations, play a crucial role in deterring fraud and holding perpetrators accountable. Upholding ethical standards within the insurance industry is essential for maintaining trust and integrity.
Insurance fraud is not only a financial crime but also carries significant legal and ethical ramifications. Individuals convicted of insurance fraud may face severe consequences, including criminal charges, civil penalties, and reputational damage. Understanding the legal frameworks at the state and federal levels, along with industry regulations, is crucial for deterring fraud and holding perpetrators accountable.
- Criminal and Civil Penalties:
- Individuals convicted of insurance fraud may face criminal charges, ranging from misdemeanors to felonies, depending on the severity of the offense and the jurisdiction.
- Criminal penalties for insurance fraud can include fines, restitution, probation, and imprisonment. In addition to criminal charges, perpetrators may also be subject to civil penalties, such as monetary damages and forfeiture of assets.
- Civil lawsuits filed by insurers or affected parties can result in significant financial liabilities for fraudsters, further deterring fraudulent behavior and providing restitution to victims.
- Reputational Damage:
- Beyond legal consequences, insurance fraud can inflict lasting reputational damage on individuals and organizations involved in fraudulent activities. A criminal conviction or civil judgment for insurance fraud can tarnish one’s reputation and credibility within the industry and the broader community.
- Reputational damage can have far-reaching implications, impacting career opportunities, business relationships, and personal relationships. It may also result in exclusion from professional associations and disciplinary actions by regulatory bodies.
- Legal Frameworks and Industry Regulations:
- Legal frameworks at the state and federal levels govern insurance fraud, defining the types of fraudulent activities, penalties for violations, and procedures for investigation and prosecution.
- Additionally, industry regulations and guidelines set forth by insurance regulators and industry associations establish standards of conduct and ethical behavior for insurers, agents, and other industry professionals.
- Compliance with legal requirements and adherence to ethical standards are essential for maintaining trust and integrity within the insurance industry. Violations of these standards can result in disciplinary actions, license revocation, and other regulatory sanctions.
- Upholding Ethical Standards:
- Upholding ethical standards within the insurance industry is essential for preserving trust and confidence among consumers, insurers, and other stakeholders. Ethical conduct promotes transparency, fairness, and accountability in all aspects of insurance operations.
- Insurance professionals are expected to adhere to principles of honesty, integrity, and professionalism in their interactions with clients, colleagues, and the public. By upholding ethical standards, insurers can foster a culture of trust and demonstrate their commitment to serving the best interests of policyholders.
Chapter 6: The Future of Insurance Fraud

The Future of Insurance Fraud As technology evolves, so do the methods employed by insurance fraudsters. Deepfake videos, synthetic identities, cyber attacks, and social engineering schemes pose new challenges for insurers and law enforcement. Innovative solutions, such as advanced analytics and artificial intelligence, are being developed to stay ahead of fraudsters. Continued collaboration and adaptation will be key in combating future trends in insurance fraud.
As technology continues to evolve at a rapid pace, the landscape of insurance fraud is also evolving, presenting new challenges and complexities for insurers and law enforcement agencies. Emerging technologies, such as deepfake videos, synthetic identities, cyber attacks, and social engineering schemes, are increasingly being employed by fraudsters to perpetrate sophisticated fraud schemes. In this chapter, we’ll explore the future of insurance fraud and discuss innovative solutions that are being developed to stay ahead of fraudsters.
- Emerging Technologies and Fraud Schemes:
- Deepfake videos: Deepfake technology enables the creation of highly realistic fake videos that can be used to manipulate visual evidence, such as staged accidents or falsified injury claims.
- Synthetic identities: Fraudsters create synthetic identities by combining real and fictitious information to establish fraudulent insurance policies or submit bogus claims.
- Cyber attacks: Cybercriminals target insurance companies and policyholders through phishing scams, ransomware attacks, and data breaches, compromising sensitive information and facilitating fraudulent activities.
- Social engineering schemes: Fraudsters exploit psychological manipulation techniques to deceive individuals into divulging confidential information or participating in fraudulent schemes, such as fake insurance policies or investment scams.
- Innovative Solutions for Fraud Detection and Prevention:
- Advanced analytics: Insurers are leveraging advanced data analytics techniques to detect patterns and anomalies indicative of fraudulent behavior. By analyzing vast amounts of data, including claims data, customer information, and external sources, insurers can identify suspicious activities and take proactive measures to prevent fraud.
- Artificial intelligence: Artificial intelligence (AI) technologies, such as machine learning algorithms, are being deployed to enhance fraud detection capabilities. AI algorithms can analyze complex data sets, detect subtle patterns, and adapt to evolving fraud schemes in real-time, enabling insurers to stay ahead of fraudsters.
- Predictive modeling: Predictive modeling techniques are used to forecast the likelihood of fraudulent behavior based on historical data and predictive indicators. By identifying high-risk individuals or transactions, insurers can allocate resources more effectively and prioritize investigations to mitigate fraud losses.
- Continued Collaboration and Adaptation:
- Collaboration between insurers, law enforcement agencies, regulatory bodies, and industry stakeholders is essential for combating future trends in insurance fraud. By sharing information, resources, and best practices, stakeholders can stay informed about emerging threats and develop coordinated strategies to address them.
- Adaptation to new technologies and fraud schemes requires ongoing investment in research, development, and training. Insurers and law enforcement agencies must continually update their tools, techniques, and knowledge to keep pace with evolving fraud tactics and safeguard the integrity of the insurance system.
Conclusion:
Insurance fraud is a complex and pervasive problem with far-reaching consequences that affect individuals, businesses, and society as a whole. However, by taking proactive steps and implementing effective detection and prevention measures, we can mitigate its impact and protect the integrity of the insurance industry.
Raising awareness about insurance fraud is crucial in educating the public about its consequences and encouraging individuals to report suspicious activities. By fostering a culture of vigilance and accountability, we can empower consumers to play an active role in combating fraud and protecting their own interests.
In addition to awareness, it’s essential to implement robust detection and prevention measures within the insurance industry. Utilizing advanced analytics, artificial intelligence, and other technological solutions can help identify fraudulent behavior and prevent fraudulent claims from being processed. By investing in these tools and continuously refining our strategies, we can stay one step ahead of fraudsters and minimize financial losses for insurers and policyholders alike.
Moreover, upholding legal and ethical standards is paramount in holding perpetrators accountable for their actions and deterring future instances of fraud. Law enforcement agencies, regulatory bodies, and industry organizations must work together to investigate and prosecute cases of insurance fraud, sending a clear message that fraudulent behavior will not be tolerated.
Ultimately, safeguarding the integrity of the insurance industry requires ongoing vigilance and collaboration among all stakeholders. By working together to raise awareness, implement effective measures, and uphold legal and ethical standards, we can protect the interests of honest policyholders and ensure that insurance remains a reliable safety net for those in need.
