Introduction
Healthcare in the United States is undergoing a profound transformation, driven by various factors such as policy changes, rising costs, and a growing emphasis on value-based care. This essay aims to delve into current trends in health insurance within the U.S., examining the impact of healthcare reform, the challenges posed by rising healthcare costs, and the ongoing shift towards value-based care delivery models.

Healthcare Reform: The Impact of Policy Changes
The Affordable Care Act (ACA), signed into law in 2010, stands as a landmark piece of legislation that has significantly reshaped the U.S. healthcare landscape. One of the key pillars of the ACA was the establishment of Health Insurance Marketplaces, where individuals and small businesses could purchase private health insurance plans. Additionally, the ACA expanded Medicaid eligibility in participating states, aiming to extend coverage to low-income individuals and families.
However, the ACA has been subject to both praise and criticism. Proponents argue that it has expanded access to healthcare coverage, reduced the uninsured rate, and provided essential consumer protections such as coverage for pre-existing conditions and essential health benefits. On the other hand, critics point to rising premiums, insurer exits from the marketplace, and regulatory burdens imposed on insurers.
The recent policy changes, including attempts to repeal or modify the ACA, have added complexity to the healthcare landscape. The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act of 2017 eliminated the individual mandate penalty, raising concerns about the stability of insurance markets and the potential for adverse selection. The COVID-19 pandemic also prompted temporary changes, such as the expansion of telehealth services and the availability of special enrollment periods.
Navigating these policy changes has been a significant challenge for insurers, providers, and consumers alike. Uncertainty surrounding the future of healthcare reform in the U.S. continues to influence insurance market dynamics and healthcare decision-making.

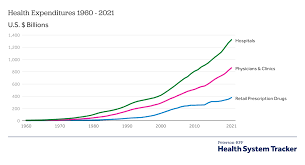
Rising Healthcare Costs: Drivers and Implications
One of the most pressing issues in U.S. healthcare is the relentless rise in healthcare costs. Numerous factors contribute to this trend, including the increasing prevalence of chronic diseases, advances in medical technology, rising prescription drug prices, and administrative expenses.
Chronic diseases such as diabetes, heart disease, and obesity account for a significant portion of healthcare spending in the U.S. The management of these conditions often requires ongoing medical care, medication, and lifestyle interventions, placing a substantial financial burden on individuals and the healthcare system as a whole.
Advancements in medical technology have undoubtedly improved patient outcomes and quality of care. However, they also come at a cost. New drugs, devices, and procedures often command high prices, contributing to overall healthcare inflation. Pharmaceutical companies, in particular, have faced scrutiny for their pricing practices, leading to calls for greater transparency and regulation.
Administrative costs associated with billing, coding, and claims processing represent another significant expense in the U.S. healthcare system. The complexity of insurance coverage, coupled with the fragmentation of the healthcare delivery system, results in inefficiencies and waste.
The implications of rising healthcare costs are far-reaching. For individuals and families, high healthcare expenses can lead to financial strain, medical debt, and barriers to accessing care. Employers grapple with the challenge of providing affordable health insurance benefits to their workforce while managing costs. Policymakers face pressure to address healthcare affordability and sustainability while ensuring access to quality care for all Americans.
The Shift Towards Value-Based Care: Promoting Quality and Efficiency
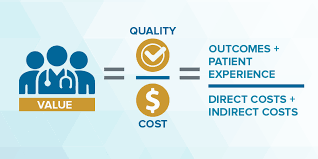
In response to the challenges posed by rising costs and variable quality in healthcare delivery, there has been a growing emphasis on value-based care models. Value-based care seeks to align incentives among payers, providers, and patients to improve health outcomes, enhance patient experience, and lower costs.
Central to value-based care is the concept of paying for value rather than volume. Traditional fee-for-service reimbursement models incentivize providers to deliver more services, regardless of their necessity or effectiveness. In contrast, value-based payment arrangements reward providers based on the quality and efficiency of care delivered.
Several value-based care models have gained traction in the U.S. healthcare system. Accountable Care Organizations (ACOs) are networks of healthcare providers who collaborate to coordinate care for a defined patient population. ACOs assume financial responsibility for the health outcomes of their patients and are incentivized to achieve cost savings while maintaining quality standards.
Bundled payment arrangements offer a fixed payment for a defined episode of care, encouraging providers to deliver services more efficiently and coordinate care across different settings. Patient-centered medical homes (PCMHs) focus on comprehensive, coordinated care for patients, with an emphasis on preventive services, chronic disease management, and care coordination.
The shift towards value-based care has implications for health insurers, who play a crucial role in facilitating these models. Insurers are increasingly partnering with providers to implement value-based payment arrangements, sharing data and resources to support care coordination and population health management efforts.
Conclusion
In conclusion, the U.S. healthcare system is experiencing a period of significant change, driven by healthcare reform efforts, rising costs, and a shift towards value-based care delivery models. Navigating these trends requires collaboration among insurers, providers, policymakers, and consumers to ensure that healthcare remains accessible, affordable, and of high quality for all Americans. While challenges persist, there are opportunities to innovate and transform the healthcare landscape to better meet the needs of patients and improve health outcomes



