Introduction
Rental property insurance, also known as landlord insurance or rental dwelling insurance, is a specialized type of insurance designed to protect property owners who rent out residential or commercial properties to tenants. This insurance provides coverage for various risks associated with renting out properties, including property damage, liability claims, loss of rental income, and legal expenses.

Importance of Rental Property Insurance
Landlord Protection:
- Property Damage: Insurance coverage protects rental properties from damage caused by perils such as fire, theft, vandalism, and natural disasters.
- Loss of Rental Income: Landlord insurance provides reimbursement for lost rental income due to covered perils, ensuring financial stability for property owners during periods of property damage or tenant displacement.
- Liability Protection: Landlords are exposed to potential liability claims arising from accidents, injuries, or property damage on the rental premises. Insurance coverage protects landlords from legal expenses and liability judgments in such cases.
Tenant Liability Coverage:
- Personal Liability: Tenant liability coverage protects tenants from financial responsibility for accidental injuries or property damage occurring on the rental property, such as slip-and-fall accidents or accidental fires.
- Additional Living Expenses: If a rental property becomes uninhabitable due to a covered peril, tenant liability coverage may provide reimbursement for additional living expenses incurred by tenants while displaced from the rental property.

Types of Coverage in Rental Property Insurance
Property Coverage:
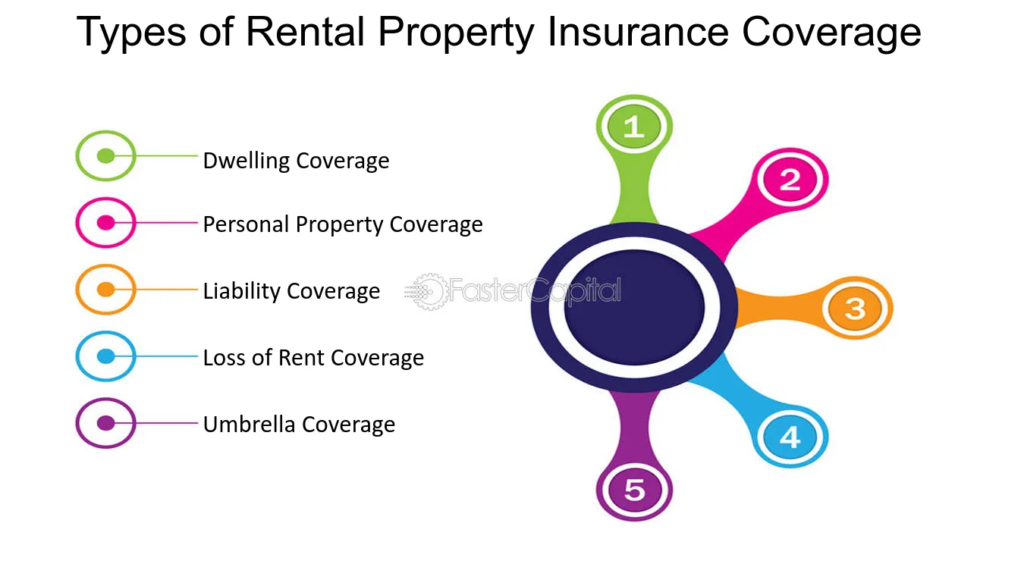
- Dwelling Coverage: Protection for the physical structure of the rental property, including the building and attached structures such as garages or sheds.
- Personal Property Coverage: Coverage for landlord-owned personal property within the rental property, such as appliances, furnishings, and equipment used for maintenance or repairs.
- Other Structures Coverage: Coverage for detached structures on the rental property, such as fences, carports, or detached garages.
Liability Coverage:
- Bodily Injury Liability: Protection against claims for bodily injuries suffered by third parties on the rental property, such as visitors or tenants’ guests.
- Property Damage Liability: Protection against claims for property damage caused by tenants or their guests on the rental property, such as accidental spills or damage to walls or flooring.
Loss of Rental Income Coverage:
- Rental Income Reimbursement: Coverage for lost rental income resulting from property damage or tenant displacement due to covered perils, such as fire or severe weather.
- Fair Rental Value: Reimbursement for the fair rental value of the rental property while it is uninhabitable due to covered perils, allowing landlords to maintain rental income during property repairs or renovations.
Considerations for Rental Property Owners
Insurance Policy Limits and Deductibles
- Coverage Limits: Landlords should carefully review policy limits to ensure adequate coverage for property replacement costs, liability claims, and loss of rental income.
- Deductibles: Landlords can choose deductible amounts, representing the portion of covered losses they are responsible for before insurance coverage applies. Higher deductibles may lower insurance premiums but require greater out-of-pocket expenses in the event of a claim.
Tenant Screening and Risk Management:
- Tenant Background Checks: Landlords should conduct thorough tenant screenings, including credit checks, rental history verification, and criminal background checks, to minimize the risk of tenant-related property damage or liability claims.
- Property Maintenance: Regular property maintenance, inspections, and repairs help prevent accidents, property damage, and liability claims, reducing the likelihood of insurance claims and premium increases.
Regulatory Considerations and Legal Requirements
State and Local Regulations:
- Insurance Requirements: Some states or municipalities may have legal requirements or regulations mandating certain types of insurance coverage for rental properties, such as liability insurance or flood insurance in high-risk areas.
- Landlord-Tenant Laws: Landlords should be aware of applicable landlord-tenant laws governing rental agreements, lease terms, eviction procedures, and tenant rights and responsibilities, which may impact insurance coverage requirements or liabilities.
Fair Housing Laws and Discrimination Protections:
- Fair Housing Act: Landlords must comply with federal fair housing laws prohibiting discrimination based on race, color, national origin, religion, sex, familial status, or disability when renting properties. Insurance policies should not discriminate against tenants based on protected characteristics or demographics.

Conclusion:
Rental property insurance plays a crucial role in safeguarding landlords and tenants from financial losses, property damage, and liability risks associated with renting properties. By obtaining comprehensive insurance coverage, landlords can protect their investments, mitigate risks, and ensure financial stability, while tenants can enjoy peace of mind knowing they are protected from liability claims and unforeseen accidents on the rental premises.




Thanks for this informative article. It was packed with information and provided great insights. For those who are keen on the world of viral real estate SEO, be sure to explore https://www.elevenviral.com to learn more.
Thanks for this enlightening article. It was very enlightening and delivered valuable knowledge. Should you be keen on viral real estate SEO, make sure to visit https://www.elevenviral.com for more information.