Introduction:
“Health insurance is a cornerstone of the healthcare system
in the United States, providing financial protection and access
to medical services for individuals and families.”
With the complexities of healthcare costs, treatments, and coverage options, understanding health insurance is essential for ensuring adequate coverage and managing healthcare expenses. This essay delves into the intricate landscape of health insurance in the USA, examining its significance, types, coverage options, pricing factors, regulations, challenges, and future trends.
Importance of Health Insurance:
Health insurance plays a critical role in promoting health equity, financial security, and access to healthcare services for individuals and communities. Several key reasons underscore the importance of health insurance:
- Access to Healthcare Services: Health insurance ensures access to essential healthcare services, including preventive care, diagnostic tests, treatments, medications, and specialty services. By covering a portion of medical expenses, health insurance enables individuals to seek timely medical care, screenings, and preventive interventions to maintain their health and well-being.

- Financial Protection: Health insurance provides financial protection against unexpected medical expenses, illness, and injury, which can incur significant costs without insurance coverage. Health insurance helps individuals and families manage healthcare costs, avoid medical debt, and protect their savings and assets from the financial burden of medical emergencies and chronic conditions.
- Health Promotion and Disease Prevention: Health insurance encourages health promotion and disease prevention initiatives by covering preventive services, screenings, vaccinations, and wellness programs. By incentivizing proactive healthcare management and early intervention, health insurance contributes to reducing healthcare costs, improving health outcomes, and preventing avoidable health complications.
- Risk Pooling and Cost Sharing: Health insurance operates on the principle of risk pooling and cost sharing, where premiums paid by policyholders are pooled together to cover medical expenses for the entire insured population. By spreading the financial risk of healthcare costs across a large and diverse pool of individuals, health insurance ensures that medical expenses are shared equitably, reducing the financial burden on individual policyholders.
Types of Health Insurance Coverage:
Health insurance policies in the USA offer various types of coverage to address different healthcare needs, preferences, and financial considerations for individuals and families. Common types of health insurance coverage include:
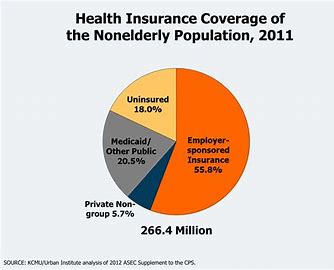
- Employer-Sponsored Health Insurance: Employer-sponsored health insurance is provided by employers to their employees as part of employee benefits packages. These health insurance plans typically offer comprehensive coverage for medical services, including hospitalization, physician visits, prescription drugs, preventive care, and mental health services. Employer-sponsored plans may be fully funded by the employer, partially funded through employee contributions, or offered as a choice among multiple plan options.
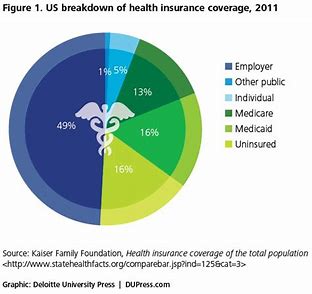
- Individual and Family Health Insurance: Individual and family health insurance plans are purchased directly by individuals or families from insurance companies or through health insurance marketplaces. These plans offer coverage for medical services for individuals and their dependents, including spouse and children. Individual and family health insurance plans may be purchased on a yearly basis or through short-term or catastrophic coverage options.
- Government-Sponsored Health Insurance: Government-sponsored health insurance programs provide coverage for specific populations, such as low-income individuals, elderly adults, children, and individuals with disabilities. Major government-sponsored health insurance programs in the USA include Medicare, Medicaid, Children’s Health Insurance Program (CHIP), and TRICARE for military personnel and their families. These programs offer subsidized or free healthcare coverage to eligible individuals based on income, age, or military service status.
- Managed Care Plans: Managed care plans are health insurance plans that coordinate and manage healthcare services for enrollees through networks of preferred providers, including primary care physicians, specialists, hospitals, and other healthcare facilities. Managed care plans aim to control costs, improve quality, and promote efficiency by emphasizing preventive care, care coordination, and utilization management strategies. Common types of managed care plans include Health Maintenance Organizations (HMOs), Preferred Provider Organizations (PPOs), and Point-of-Service (POS) plans.
- High-Deductible Health Plans (HDHPs) with Health Savings Accounts (HSAs): High-deductible health plans (HDHPs) are health insurance plans that feature higher deductibles and lower premiums compared to traditional health insurance plans. HDHPs are paired with Health Savings Accounts (HSAs), which allow individuals to save and invest pre-tax dollars to pay for qualified medical expenses. HDHPs with HSAs offer tax advantages, flexibility, and control over healthcare spending while providing coverage for catastrophic medical expenses.
Coverage Options and Considerations:
When selecting health insurance coverage, individuals and families should consider several factors to ensure adequate protection, affordability, and alignment with their healthcare needs and preferences:
- Coverage Benefits and Services: Evaluate the comprehensiveness of coverage benefits and services offered by health insurance plans, including hospitalization, physician visits, prescription drugs, preventive care, mental health services, maternity care, and specialty care. Consider the scope of coverage for specific medical conditions, treatments, and healthcare providers to ensure access to necessary services.
- Cost-Sharing Features: Understand the cost-sharing features of health insurance plans, including premiums, deductibles, copayments, coinsurance, and out-of-pocket maximums. Compare the total cost of coverage, including premiums and out-of-pocket expenses, to determine affordability and value for money. Consider how cost-sharing features affect monthly budgeting, healthcare utilization, and financial risk protection.
- Provider Networks: Review the provider networks associated with health insurance plans to ensure access to preferred healthcare providers, including primary care physicians, specialists, hospitals, and other healthcare facilities. Determine whether providers are in-network or out-of-network, as out-of-network services may result in higher out-of-pocket costs or coverage limitations.
- Prescription Drug Coverage: Assess the prescription drug coverage offered by health insurance plans, including formularies, copayments, and coverage tiers for generic and brand-name medications. Evaluate whether prescription drugs are covered under the plan’s pharmacy benefits or through separate prescription drug plans (Part D) for Medicare beneficiaries.
- Coverage for Pre-Existing Conditions: Determine how health insurance plans define and handle pre-existing conditions, which are health conditions or symptoms existing before the policy’s effective date. Review waiting periods, coverage limitations, or exclusions for pre-existing conditions to understand potential restrictions on coverage for chronic conditions or ongoing medical treatments.
- Value-Added Benefits: Consider additional benefits and services offered by health insurance plans, such as wellness programs, telemedicine services, health coaching, disease management, and preventive screenings. Value-added benefits may enhance the overall healthcare experience, promote health promotion, and support chronic disease management efforts.
Key Markets and Trends in Health Insurance:
The health insurance market in the USA is dynamic and evolving, influenced by various market trends, policy reforms, technological innovations, and consumer preferences:
- Market Consolidation and Mergers: The health insurance industry has witnessed significant consolidation and mergers among insurers, leading to the formation of large conglomerates and diversified healthcare companies. Mergers and acquisitions aim to achieve economies of scale, expand market presence, and enhance competitive advantages in the rapidly evolving healthcare landscape. Market consolidation may impact competition, pricing, and consumer choice in certain markets.
- Value-Based Care and Population Health Management: Insurers and healthcare providers are shifting towards value-based care models and population health management strategies to improve health outcomes, reduce costs, and enhance patient experience. Value-based care emphasizes preventive care, care coordination, chronic disease management, and outcome-based reimbursement arrangements. Insurers are incentivizing providers to deliver high-quality, cost-effective care through value-based contracts, accountable care organizations (ACOs), and bundled payment models.
- Digital Transformation and Telehealth Adoption: Advancements in technology, digital health platforms, and telemedicine solutions are transforming the delivery of healthcare services and patient engagement. Insurers are leveraging digital tools, electronic health records (EHRs), mobile apps, and telehealth platforms to enhance access to care, improve care coordination, and facilitate remote consultations, monitoring, and follow-up care. Telehealth adoption has surged during the COVID-19 pandemic, driving expansion of virtual care options and reimbursement policies.
- Consumer-Centric Solutions and Personalization: Insurers are focusing on consumer-centric solutions and personalized insurance offerings to meet individuals’ unique healthcare needs, preferences, and lifestyles. Personalization features may include flexible coverage options, wellness incentives, value-added services, and digital tools for health management and decision-making. Insurers are investing in data analytics, predictive modeling, and artificial intelligence to tailor insurance products, pricing, and communication strategies to individual consumer profiles.
- Regulatory Reforms and Policy Initiatives: Health insurance markets are influenced by regulatory reforms, policy initiatives, and legislative changes aimed at expanding coverage, controlling costs, and improving healthcare quality and access. Recent policy developments include the Affordable Care Act (ACA), which expanded access to health insurance coverage through insurance marketplaces, Medicaid expansion, and consumer protections such as guaranteed issue and essential health benefits. Regulatory reforms focus on addressing healthcare disparities, promoting value-based care, and enhancing transparency and consumer choice in insurance markets.

Conclusion:
Health insurance plays a vital role in promoting access to healthcare services, financial protection, and health equity for individuals and families in the USA. By offering coverage for medical expenses, preventive care, and value-added services, health insurance helps individuals manage healthcare costs, navigate the complexities of the healthcare system, and achieve better health outcomes. As the healthcare landscape continues to evolve, insurers, policymakers, and stakeholders must collaborate to address emerging challenges, promote innovation, and ensure affordable, accessible, and high-quality healthcare coverage for all Americans. Through continuous adaptation, consumer empowerment, and regulatory oversight, health insurance remains a cornerstone of the nation’s healthcare infrastructure, supporting individuals’ health and well-being throughout their lifetimes.



