Introduction:
Life insurance serves as a cornerstone of financial planning
and risk management for individuals and families in the United States,
providing protection, security, and peace of mind in the face
of life’s uncertainties.
With its diverse range of products and coverage options, life insurance offers financial support to beneficiaries in the event of the policyholder’s death, ensuring continuity of income, debt repayment, and wealth preservation. This essay explores the intricate landscape of life insurance in the USA, examining its significance, types, coverage options, pricing factors, regulations, challenges, and future trends.
Importance of Life Insurance:
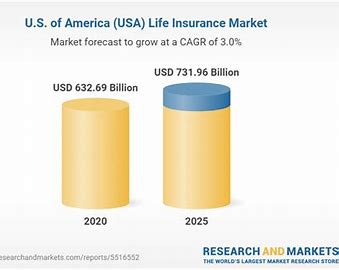
Life insurance plays a vital role in securing financial stability, protecting loved ones, and fulfilling long-term financial goals for policyholders and their families. Several key reasons underscore the importance of life insurance:
- Financial Protection: Life insurance provides financial protection and security for beneficiaries by paying out a death benefit upon the policyholder’s death. The death benefit can be used to replace lost income, cover living expenses, settle outstanding debts, such as mortgages, loans, and medical bills, and maintain the policyholder’s standard of living. Life insurance ensures that loved ones are financially supported and provided for in the event of the policyholder’s premature death.
- Wealth Preservation: Life insurance serves as a wealth preservation tool for policyholders, helping to preserve and transfer assets to future generations. Life insurance proceeds can be used to pay estate taxes, inheritance taxes, and final expenses, allowing policyholders to pass on their wealth and assets to heirs and beneficiaries without burdening them with financial obligations or liquidating assets. Life insurance facilitates intergenerational wealth transfer and estate planning objectives.
- Estate Planning: Life insurance plays a crucial role in estate planning strategies, providing liquidity, flexibility, and tax-efficient solutions for transferring assets and addressing inheritance issues. Life insurance proceeds are generally income tax-free to beneficiaries and can be used to equalize inheritances among heirs, provide for charitable bequests, fund trusts, or cover estate settlement costs. Life insurance complements other estate planning tools, such as wills, trusts, and powers of attorney, to achieve the policyholder’s legacy and philanthropic goals.
- Income Replacement: Life insurance serves as a safety net for dependents and beneficiaries who rely on the policyholder’s income for financial support. In the event of the policyholder’s death, life insurance provides a source of replacement income to cover ongoing living expenses, educational costs, childcare expenses, and other financial needs. Life insurance ensures that survivors can maintain their standard of living and achieve their long-term financial goals without experiencing financial hardship or instability.
- Business Continuity: Life insurance is essential for business owners and key employees to protect business interests, ensure continuity of operations, and mitigate financial risks associated with the loss of key personnel. Key person insurance provides coverage for key employees whose death or disability could significantly impact business revenue, profitability, or operations. Buy-sell agreements funded by life insurance facilitate business succession planning and transfer ownership interests among partners or shareholders in the event of a business owner’s death.
Types of Life Insurance Coverage:
Life insurance policies in the USA offer various types of coverage to meet different financial planning needs, risk preferences, and budgetary constraints for policyholders and beneficiaries. Common types of life insurance coverage include:

- Term Life Insurance: Term life insurance provides coverage for a specified period, known as the term of the policy, typically ranging from 5 to 30 years. Term life insurance offers temporary protection and death benefit coverage at a fixed premium for the duration of the term. If the policyholder dies during the term, the insurance company pays out a death benefit to the beneficiaries. Term life insurance is affordable, straightforward, and suitable for individuals seeking temporary coverage to protect against premature death, such as mortgage protection, income replacement, or educational expenses.
- Whole Life Insurance: Whole life insurance, also known as permanent life insurance, provides coverage for the policyholder’s entire lifetime, as long as premiums are paid as scheduled. Whole life insurance offers guaranteed death benefit protection, cash value accumulation, and level premiums for the duration of the policy. Cash value growth is tax-deferred and can be accessed through policy loans or withdrawals for supplemental income, retirement planning, or emergency expenses. Whole life insurance provides long-term financial security, estate planning benefits, and cash value accumulation for policyholders and beneficiaries.
- Universal Life Insurance: Universal life insurance is a flexible permanent life insurance product that offers customizable death benefit protection, premium flexibility, and cash value accumulation. Universal life insurance policies consist of two components: a death benefit and a cash value account. Policyholders can adjust premium payments, death benefit amounts, and cash value allocation to suit their changing financial needs and goals. Universal life insurance provides policyholders with control, flexibility, and tax-advantaged wealth accumulation options while ensuring long-term financial protection for beneficiaries.
- Variable Life Insurance: Variable life insurance is a permanent life insurance product that allows policyholders to allocate premiums to investment accounts composed of mutual funds or variable subaccounts. The cash value accumulation and death benefit of variable life insurance are tied to the performance of the underlying investment portfolio, subject to market fluctuations and investment risk. Policyholders have the opportunity to earn higher returns and build cash value through investment growth, but they also bear the risk of investment losses. Variable life insurance offers potential for wealth accumulation and asset growth, along with death benefit protection and investment flexibility.
- Indexed Universal Life Insurance: Indexed universal life insurance combines the features of universal life insurance with the potential for cash value growth linked to the performance of stock market indices, such as the S&P 500. Indexed universal life insurance offers policyholders the opportunity to participate in market gains while providing downside protection against investment losses. Cash value accumulation is tied to the performance of the selected index, with a minimum guaranteed interest rate and downside protection limits. Indexed universal life insurance offers policyholders flexibility, growth potential, and downside protection, along with death benefit coverage and tax advantages.
Coverage Options and Considerations:

When selecting life insurance coverage, individuals and families should consider several factors to ensure adequate protection, affordability, and alignment with their financial planning objectives, risk tolerance, and future needs:
- Coverage Amount: Determine the appropriate coverage amount needed to meet the financial needs and goals of beneficiaries in the event of the policyholder’s death. Consider factors such as income replacement needs, outstanding debts, mortgage obligations, educational expenses, funeral costs, estate taxes, and future financial goals when calculating the desired death benefit amount. Ensure that the coverage amount is sufficient to provide for beneficiaries’ ongoing financial security and maintain their standard of living.
- Policy Duration: Choose the appropriate policy duration or term length based on the policyholder’s financial planning horizon, life stage, and coverage needs. Term life insurance is suitable for short-term protection needs, such as income replacement during the working years, mortgage payoff, or educational expenses. Permanent life insurance offers lifetime coverage and cash value accumulation, making it suitable for long-term financial planning, estate protection, and legacy planning objectives.
- Premium Affordability: Evaluate the affordability of life insurance premiums based on the policyholder’s budget, income level, and financial priorities. Consider premium payment options, such as annual, semi-annual, quarterly, or monthly payments, and choose a payment frequency that aligns with cash flow and budgeting preferences. Compare premium quotes from multiple insurers to find competitive rates and cost-effective coverage options while ensuring that premiums remain affordable over the life of the policy.
- Cash Value Accumulation: Consider the cash value accumulation potential of permanent life insurance policies, such as whole life insurance, universal life insurance, variable life insurance, or indexed universal life insurance. Evaluate the policy’s cash value growth potential, guaranteed interest rates, investment options, and surrender charges to determine the suitability of the policy for wealth accumulation, retirement planning, or supplemental income needs. Cash value accumulation provides policyholders with access to tax-deferred savings and financial flexibility during their lifetime.
- Policy Riders and Endorsements: Explore optional riders and endorsements offered by insurers to customize life insurance coverage and address specific financial planning needs and concerns. Common riders may include accelerated death benefit riders, which provide access to a portion of the death benefit in the event of terminal illness, chronic illness, or long-term care needs. Other riders may include waiver of premium riders, accidental death benefit riders, child term riders, or guaranteed insurability riders. Evaluate the cost, benefits, and suitability of riders to enhance coverage and tailor insurance protection to individual circumstances.
- Underwriting Considerations: Understand the underwriting process and eligibility requirements for life insurance coverage, including medical underwriting, risk assessment, and health screenings. Insurers evaluate applicants’ age, health status, medical history, lifestyle factors, and occupation to determine insurability and premium rates. Applicants may be required to undergo medical exams, laboratory tests, or health questionnaires to assess their health risk profile and qualify for coverage. Consider pre-existing medical conditions, family health history, and lifestyle habits when applying for life insurance coverage to ensure accurate underwriting and fair pricing.
Key Markets and Trends in Life Insurance:
The life insurance market in the USA is dynamic and evolving, influenced by various market trends, demographic shifts, regulatory changes, technological innovations, and consumer preferences:
- Demographic Trends: The life insurance industry faces demographic challenges stemming from population aging, declining birth rates, and shifting consumer preferences among younger generations. Insurers are adapting product offerings, marketing strategies, and distribution channels to appeal to diverse demographic segments, such as millennials, Gen Xers, and baby boomers. Demand for life insurance coverage remains strong among families, homeowners, and individuals seeking financial protection, estate planning, and retirement income solutions.
- Digital Transformation: Advancements in technology, digital platforms, and online distribution channels are transforming the life insurance industry’s customer experience, underwriting processes, and policy administration capabilities. Insurers are investing in digital tools, mobile apps, and online portals to streamline policy sales, underwriting, claims processing, and customer service interactions. Digital innovations enhance accessibility, convenience, and transparency for policyholders, agents, and insurance professionals, facilitating faster transactions and improved communication.
- Insurtech Innovation: Insurtech startups are disrupting the life insurance industry with innovative solutions for customer engagement, risk assessment, underwriting automation, and product distribution. Insurtech companies leverage artificial intelligence, machine learning, data analytics, and predictive modeling to enhance risk selection, improve pricing accuracy, and personalize insurance offerings. Insurtech platforms offer consumers simplified online purchasing experiences, algorithmic underwriting decisions, and real-time policy management capabilities, driving efficiency and innovation in the insurance value chain.
- Behavioral Economics and Wellness Incentives: Insurers are incorporating behavioral economics principles and wellness incentives into life insurance products to encourage healthy lifestyle behaviors, risk reduction, and preventive healthcare measures. Wellness programs offer policyholders incentives, rewards, or discounts for participating in health screenings, fitness activities, and wellness initiatives aimed at improving overall health outcomes and reducing insurance risks. Behavioral-based underwriting models assess individuals’ lifestyle habits, adherence to preventive care, and health-related behaviors to tailor insurance coverage and pricing based on risk factors.
- Regulatory Reforms and Consumer Protection: Life insurance markets are subject to regulatory oversight, consumer protection laws, and compliance requirements aimed at ensuring fair treatment, transparency, and market stability. Regulatory reforms focus on consumer disclosures, suitability standards, policyholder protections, and market conduct practices to enhance consumer confidence and trust in the insurance industry. Regulatory initiatives address issues such as sales practices, policy illustrations, replacement guidelines, and premium rate stability to safeguard policyholders’ interests and promote market integrity.
Conclusion:
Life insurance serves as a foundational pillar of financial planning, risk management, and wealth protection for individuals, families, and businesses in the USA. By offering death benefit protection, cash value accumulation, and financial security, life insurance helps policyholders achieve their long-term financial goals, protect loved ones, and build a legacy for future generations. As the life insurance industry continues to evolve, insurers, regulators, and stakeholders must collaborate to address emerging challenges, promote innovation, and enhance consumer protection. Through innovative product offerings, digital transformation, and regulatory compliance, life insurance remains a fundamental tool for securing futures, ensuring financial stability, and providing peace of mind for policyholders and beneficiaries alike.




Many thanks for this informative article. It was packed with information and delivered a lot of useful information. Should you be keen on the world of viral real estate SEO, don’t hesitate to explore https://www.elevenviral.com to learn more.